Scientists Discover Vast Reef Behind The Great Barrier Reef
James Cook University, University of Sydney and Queensland University of Technology scientists working with laser data from the Royal Australian Navy have discovered a vast reef behind the familiar Great Barrier Reef.
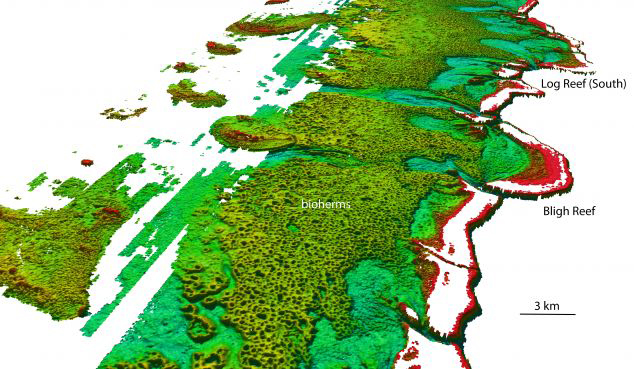
JCU’s Dr Robin Beaman says the high-resolution seafloor data provided by LiDAR-equipped aircraft have revealed great fields of unusual donut-shaped circular mounds, each 200-300 meters across and up to 10 meters deep at the center.
Halimeda is a green macroalgae composed of calcified leaf-like segments. As these plants die, these segments turn white and accumulate over thousands of years forming thick mounds called bioherms. Where these plants have died, A living layer of Halimeda algae covers the bioherms and stretches across an area of 6095 km2 on the landward side of the reef.
Halimedia Photo Credit: Live Aquaria
Although the Halimeda habitat was previously known to GBR scientists, this new study shows the reefs are three times larger and more complex than previously thought.
Scientists used high-resolution airborne LiDAR and multi-beam bathymetry datasets to gain a more accurate calculation of the bioherms. Previous studies of the reef used sediment grabs, coring and seismic profiling, and the distribution was estimated at 2000 km2 using interpolation from echo-sounder profiles.
“We’ve known about these geological structures in the northern Great Barrier Reef since the 1970s and 80s, but never before has the true nature of their shape, size and vast scale been revealed,” he said.
Dr Beaman said it was an astounding revelation. “The deeper seafloor behind the familiar coral reefs amazed us.”
The fields of circular donut-shaped rings are Halimeda bioherms, large reef-like geological structures formed by the growth of Halimeda, a common green algae composed of living calcified segments.
These form small limestone flakes on death, looking much like white cornflakes. Over time these flakes build up into large reef-like mounds, or bioherms.
Mardi McNeil from Queensland University of Technology and lead author on the new research paper, said their extent is vast.
“We’ve now mapped over 6000 square kilometres. That’s three times the previously estimated size, spanning from the Torres Strait to just north of Port Douglas. They clearly form a significant inter-reef habitat which covers an area greater than the adjacent coral reefs.”
Associate Professor Jody Webster from the University of Sydney, said the revelations about the extent of the bioherm field make questions over its vulnerability to climate change even more pressing.
“As a calcifying organism, Halimeda may be susceptible to ocean acidification and warming. Have the Halimeda bioherms been impacted, and if so to what extent?”
Dr Beaman said the discovery also opened up many other new avenues of research.
“For instance, what do the 10-20 metre thick sediments of the bioherms tell us about past climate and environmental change on the Great Barrier Reef over this 10,000 year time-scale? And, what is the finer-scale pattern of modern marine life found within and around the bioherms now that we understand their true shape?”
He said future research would require sediment coring, sub-surface geophysical surveys, and employing autonomous underwater vehicle technologies to unravel the physical, chemical and biological processes of the structures. For more information visit James Cook University release.
Read more here: Aqua Nerd
Comments are closed.